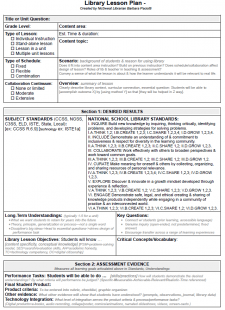
In our modern globally-connected world, reading is the most essential literacy for anyone.
In our modern globally-connected world, reading is the most essential literacy for anyone.
There are probably very few professions now where you are going to be able to make a living if you are not capable of reading and understanding instructions or rules about your business. (Steve Gardiner, Gamber-Thompson, 2019.)
So, when School Librarian listservs and Facebook groups post a question about how to promote more student reading, we jump in with dozens of suggestions. As I read, I rarely see evidence of an increase in student achievement, yet that is our most important purpose as a School Librarian! So how can a School Librarian identify the best way to increase student reading achievement?
WHY SOME READING PROMOTIONS MAY NOT WORK
Unfortunately, some honestly sincere suggestions may not have a significant impact on student reading achievement, because they are based on extrinsic rewards, rather than giving students the intrinsic motivation to read.
Gimmicks like food or party rewards, tokens for quantity reading, and other incentives may seem to get students excited, but I believe the results of success from such promotions are skewed. Prolific readers jump at such ploys because they know they can “win,” whereas nonreaders see no gratifying advantage to participate—the reward simply doesn’t override their reluctance to read. Not that we should cease doing it; just that we shouldn’t expect it to make a difference in reading proficiency or achievement for students.
Fancy bulletin boards and book displays also seem to excite students to read more because we’re inundated with requests from students to borrow the books shown. While these exhibits are a valuable way to boost the visibility of the school library, they still won’t increase reading proficiency because most nonreaders aren’t motivated enough to look at the titles, let alone read them.
As more schools push English Language Arts teachers to create classroom libraries, School Librarians lament the limitation of reading choices and the decrease in library circulation. The more important point is that having books in the classroom doesn’t necessarily boost student reading achievement. It depends on how a teacher implements reading activities; improperly done it can discourage reluctant readers even more, rather than make them more proficient.
THE ONE READING STRATEGY THAT REALLY WORKS
 To make a real impact on student reading and a commensurate improvement in reading achievement, School Librarians can push for Sustained Silent Reading. There is substantial research that SSR works to improve student reading proficiency and comprehension, in spite of criticism: “When the research facts are unraveled from misinterpretations and opinion, we find that SSR is … supported by research.” (Garan & Devoogd, p336.)
To make a real impact on student reading and a commensurate improvement in reading achievement, School Librarians can push for Sustained Silent Reading. There is substantial research that SSR works to improve student reading proficiency and comprehension, in spite of criticism: “When the research facts are unraveled from misinterpretations and opinion, we find that SSR is … supported by research.” (Garan & Devoogd, p336.)
No matter your feelings about standardized reading tests—state, national, or international—they are a valid indicator of reading proficiency and comprehension. At the time my middle school implemented SSR, our state reading scores were the lowest in the district, but over a 4-year period they increased by nearly 20 points. This included special populations, of which we had more than the other middle schools: highest diversity, highest poverty, highest transience. Our results astonished district administrators into pushing for SSR in all middle schools!
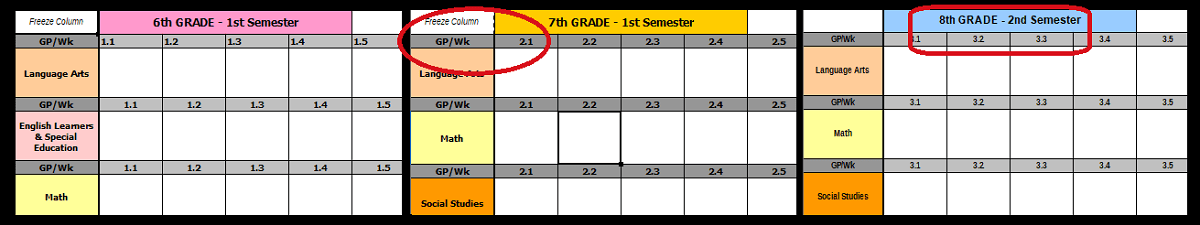
One major component of our approach is regularly scheduled full-period visits to the school library for Sustained Silent Reading. Each grade level chooses a certain day of the week, and they visit every other week for the entire school year. ELA teachers still provide short in-class read time, but having longer, continuous reading sessions in the library enables teachers to include more reading comprehension skills in the classroom.
 As the School Librarian, I implemented 5 strategies that heighten the impact of SSR. These strategies are the focus of my school library orientations, introducing them to new-to-the-school students and reviewing them with returning students.
As the School Librarian, I implemented 5 strategies that heighten the impact of SSR. These strategies are the focus of my school library orientations, introducing them to new-to-the-school students and reviewing them with returning students.
- Fiction Subject Spine Labels – Krashen’s evaluation of SSR research found that having interesting books was critical for success with SSR, and we must accept that most students have a preference for the kind of stories they like to read. So, adding Fiction Subject spine labels to books makes a huge difference for student buy-in of SSR. I eventually added color-coded transparent labels over the call number label and distributed books into Subject sections to make book selection even easier.
linebreak 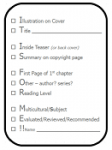 IT IS FOR ME checklist – This form—and the short video I created to introduce it—helps students quickly scan a book so they can decide if it’s right for them. They take one with them to the shelves at every library visit, and ELA teachers collect them for a no-stress daily participation grade.
IT IS FOR ME checklist – This form—and the short video I created to introduce it—helps students quickly scan a book so they can decide if it’s right for them. They take one with them to the shelves at every library visit, and ELA teachers collect them for a no-stress daily participation grade.
Get the checklist from my FREE Librarian Resources page!
linebreak- The 5-Finger Test – For SSR to succeed with reluctant and/or struggling readers, their book choice must be at an appropriate reading level, but we don’t want to label books. The 5-finger test helps them: Turning to the middle of the book they read the two pages in front of them, holding up a finger for each word they come to that they don’t know. If they reach 5 fingers, the book is a bit too hard and they need to find a better (don’t say easier) book.
linebreak - 20-page Guide – Students only read freely a story they like, and nothing is more discouraging than requiring students to finish a book they don’t like. I tell students to allow the author to introduce the story setting and characters, so read 20 pages and if they still don’t like a book, then definitely return it and get a different one—that’s why we offer them thousands of choices in the school library!
linebreak - Silent Invited Book Checkout – This is the one that made the most difference! I give students plenty of time to find a good book—at least 5-7 minutes–and they return to the table for Sustained Silent Reading time. This allows students to become immersed in their book so they’re more likely to continue reading and finish it. After a while, I walk over to a pair of tables and signal students to come up for book checkout. They line up single file, still reading. When finished with that group, I invite another pair of tables for checkout, continuing until all tables are done. Just a few students at a time for checkout ensures an orderly & quiet environment and I can do 2 full classes in about 10 minutes. Typically students have about 30 minutes total for SSR.
ENHANCE SSR BY SUPPORTING CLASSROOM LEARNING
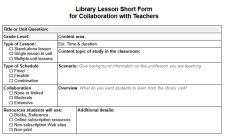
Sometimes, I augment an ELA library visit with a short lesson to support classroom learning, which research confirms can make a difference in student reading achievement.
Indeed, having librarians take an instructional role — and do it well — has been correlated with students’ success at meeting academic standards. … [when] librarians did an “excellent” job teaching to state reading and writing standards, students in their schools were more likely to excel and less likely to score poorly on corresponding tests. (Lance & Schwarz, 2012 in Lance & Kachel, 2018.)
Rendering “do it well” and “an excellent job” demands a School Librarian know best practices of SSR in order to bridge it with ongoing classroom instruction:
…reading widely across selected literary genres, setting personal goals for completing the reading of books within a timeframe, conferring with their teacher, and completing response projects to share the books they read with others. (Garan & Devoogd, p 342.)
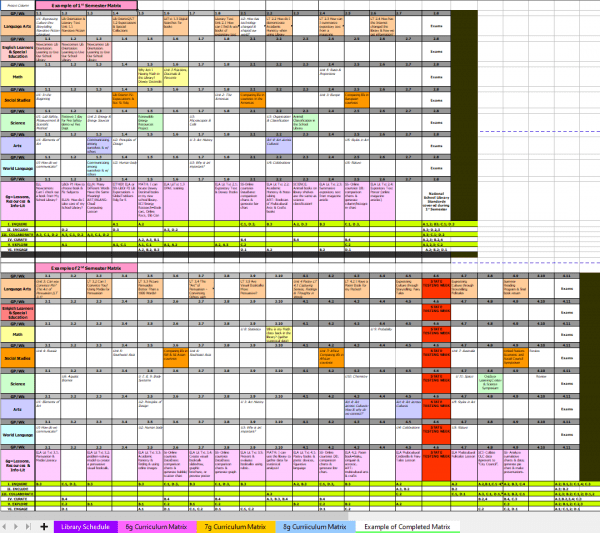
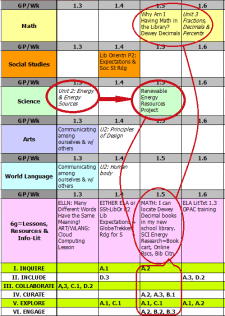
 Giving students a glimpse into the world of books expands their appreciation for reading and the school library. That’s the hook for my 3-Lesson Reading Fiction Books Unit that supports 6g ELA study of narrative literary text. Each of the lessons incorporates one practice mentioned above:
Giving students a glimpse into the world of books expands their appreciation for reading and the school library. That’s the hook for my 3-Lesson Reading Fiction Books Unit that supports 6g ELA study of narrative literary text. Each of the lessons incorporates one practice mentioned above:
- How do folktales relate to fiction Subjects? helps students identify the characteristics of different kinds of fiction stories by associating them with types of folktales they learned about in elementary school. It incites students to try out different “Subjects” of fiction they hadn’t considered before.
- How can I find the “best” books to read? introduces national book awards, multicultural books, and state awards & reading lists, and provides a personal Reading Record for students to track the books they read.
- How can I help others find a good book to read? uses the 5 elements of fiction literature and a 3×5 index card to help students create a simple book “quick-talk” that they can share with peers.
The beauty of this unit is that it can be used as a collaborative ELA lesson or by those School Librarians who are “in the rotation” with regularly scheduled library periods. It’s a perfect follow-up to the library orientation, with enriching activities that continue to promote reading.
TIME TO READ IS THE GREATEST GIFT
The greatest gift a School Librarian can give students is time: plenty of time to find a good book to read, and then plenty of time to begin reading and become immersed in the story. When we provide a guide to make browsing time profitable and offer evidence that Sustained Silent Reading works, we can convince teachers that this “time” is necessary for students to improve their reading achievement. The true value of Sustained Silent Reading is expressed by teacher Steve Gardiner:
Then my students would come back from college and say things like, “Wow, I got into this engineering program and I never imagined how much I was going to have to read for it. Thank you so much for teaching me, giving me that SSR that helped me learn that I was a reader, that I could read a full book from start to finish, and that I could stick with reading projects.” They would say things like, “It’s been so valuable for me now.” Dozens and dozens of students came back and thanked me for SSR. (Gamber-Thompson, 2019.)
![]()
Gamber-Thompson, Liana. How Sustained Silent Reading Keeps Students Curious and Engaged. EdSurge Oct 7, 2019
https://www.edsurge.com/news/2019-10-07-how-sustained-silent-reading-keeps-students-curious-and-engaged Accessed December 27, 2021.
Garan, Elaine & Devoogd, Glenn. (2008). The Benefits of Sustained Silent Reading: Scientific Research and Common Sense Converge. Reading Teacher – READ TEACH. 62. 336-344. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250055938_The_Benefits_of_Sustained_Silent_Reading_Scientific_Research_and_Common_Sense_Converge Accessed December 30, 2021.
Krashen, Stephen. Non-Engagement in Sustained Silent Reading: How extensive is it? What can it teach us? Colorado Reading Council Journal 2011, vol 22: 5-10. http://www.sdkrashen.com/content/articles/non-engagement_in_ssr.pdf Accessed December 28, 2021.
Lance, Keith Curry, and Debra Kachel. 2018. “Why School Librarians Matter: What Years of Research Tell Us.” Phi Delta Kappan Online. http://www.kappanonline.org/lance-kachel-school-librarians-matter-years-research Accessed December 27, 2021.