School Librarians know that literacy is more than just reading and writing. It includes disciplinary, information, digital, and media literacies. Media Literacy is especially important because it incorporates all other literacies and directly impacts us through news, films, television shows, websites, music, and social media.
School Librarians know that literacy is more than just reading and writing. It includes disciplinary, information, digital, and media literacies. Media Literacy is especially important because it incorporates all other literacies and directly impacts us through news, films, television shows, websites, music, and social media.
My concern about media literacy lessons is that so many focus on the negative side of media and communication. It leads students to believe they must be suspicious of everything, and perform intricate analyses of every media message. Such stress can result in the opposite reaction than we want—students turn off and ignore caution completely!
I believe students learn far more—and better—when we focus on conceptual understandings and give them a positive activity to demonstrate those concepts. When they use their learning to create something original, concepts become deeply embedded into their knowledge base and they will then automatically gauge the intent of any media message. Such is the thinking behind my Library Lesson Unit for teaching Media Literacy.
MEDIA LITERACY CONCEPTS
The Center for Media Literacy, which has 25 years of experience in this field, puts forward key questions students can ask when viewing a media message, and core concepts that emerge from those questions:
| Categories | Key Questions | Core Concepts |
| Authorship | Who created this message? | All media messages are ‘constructed.’ |
| Purpose | Why is this message being sent? | Most media messages are organized to gain profit and/or power. |
| Format | What creative techniques are used to attract my attention? | Media messages are constructed using a creative language with its own rules. |
| Audience | How might different people understand this message differently? | Different people experience the same media message differently. |
| Content | What values, lifestyles, and points of view are represented in, or omitted from, this message? | Media have embedded values and points of view. |
For my middle school media literacy units I plan my lessons based on age appropriateness and topical content of the grade level. For 6th grade lessons I introduce, what I consider to be, the three foundation questions and concepts—on Authorship, Purpose, and Format. I add Audience for 7th grade because that age/grade is consumed with identity, and add Content for 8th grade because it embodies power & influence, a focus of 8g ELA. In this way we cover all 5 questions & concepts during a student’s time in our middle school.
INTRODUCING MEDIA LITERACY
One thing I’ve discovered about middle schoolers is that they will watch a video of a slideshow more attentively than listen to me show it. So, to introduce Media Literacy and the first 3 Key Questions & Core Concepts to 6th graders, I created a short, 3-minute video.
(If you like this, feel free to use it with your students to begin their exploration of media lit.)
MEDIA LITERACY PERFORMANCE TASK
 Since media literacy has fairly complex concepts, I choose a performance task related to something students are already familiar with, one that extends their prior knowledge. My first two 6th grade units (fiction books and informational resources) are closely aligned with English Language Arts content, and focus on reading and summarization (a low-performing area on state reading tests) through graduated forms of booktalks. The media literacy performance task builds on those previous units by having students create a media message in the form of a visual booktalk, which aligns with their ELA study of persuasive text.
Since media literacy has fairly complex concepts, I choose a performance task related to something students are already familiar with, one that extends their prior knowledge. My first two 6th grade units (fiction books and informational resources) are closely aligned with English Language Arts content, and focus on reading and summarization (a low-performing area on state reading tests) through graduated forms of booktalks. The media literacy performance task builds on those previous units by having students create a media message in the form of a visual booktalk, which aligns with their ELA study of persuasive text.
It’s important for each library visit to have a hands-on activity that practices what students are learning. So, I use the questions & concepts from the video to introduce students to the visual booktalk project. A Combination Notes activity helps them visualize their library book’s story through a summary, descriptive words and image sketches, and a persuasive appeal.
I also believe students need to have choices for assessment products, so I offer 3 options for the product: an 11×17 Book Preview Poster, a letter-sized trifold Graphic Booktalk Brochure, and a Timed Slideshow Booktalk that utilizes technology.
DEVELOPING THE MEDIA LITERACY UNIT
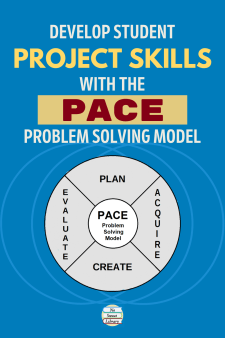 Since my media literacy unit is project/product oriented, I introduce students to a very simple problem solving model (incorporating information literacy) called PACE: Plan, Acquire, Create, Evaluate. It provides a structure for the unit lessons, with each step of PACE as a library visit that advances the project’s development from start to finish.
Since my media literacy unit is project/product oriented, I introduce students to a very simple problem solving model (incorporating information literacy) called PACE: Plan, Acquire, Create, Evaluate. It provides a structure for the unit lessons, with each step of PACE as a library visit that advances the project’s development from start to finish.
This unit also conforms to my personal strategy for all Library Lessons: “teach only the information or skill they need for the task at hand.” Consequently each lesson’s instruction is short enough to give students plenty of time to work on each step of their chosen project during the class periods. This consideration assures equity, in that no student is disadvantaged by a home situation or economics, and I (and the teacher, if a collaboration) can assist individuals throughout.
I weave the questions & concepts vocabulary into instruction, and directly revisit them in the fourth “Evaluate” visit. This quick review helps students apply their conceptual understanding by evaluating two media message booktalks that are a different type than the one they chose.
FOCUSING ON THE POSITIVE
My positive approach to media literacy lessons has the same effect on students as my Academic Honesty unit. Students are more relaxed about learning and eager to work on their assignment; they don’t exhibit the anxiety induced from emphasizing negative aspects of concepts, principles, and practices.
I’m confident that when School Librarians use an affirmative method for teaching the 5 essential literacies, they will build better relationships with students and with teachers. That surely fosters more collaborative opportunities with teachers and higher achievement for students.
 |
 |
 |