 Plagiarism. A “hot” word when teachers assign a research project to students. College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards refer to plagiarism, and Common Core State Standards refer to plagiarism and bibliographic citation, so students invariably get a (boring) lesson about these topics when they begin research.
Plagiarism. A “hot” word when teachers assign a research project to students. College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards refer to plagiarism, and Common Core State Standards refer to plagiarism and bibliographic citation, so students invariably get a (boring) lesson about these topics when they begin research.
Unfortunately, those topics relate only to documentation, so that is typically all that teachers teach. However, according to the AASL National School Library Standards, School Librarians are charged with teaching a much wider range of concepts:
- VI.A. The school library serves as a context in which the school librarian ensures that the school community is aware of the guidelines for safe, ethical, and legal use of information by:
- 1. Educating the school community on the ethical use of information and the intellectual property of others.
- 3. Embedding legal, ethical, and social responsibility concepts into the inquiry and information seeking processes.
So, School Librarians provide students with a deep conceptual understanding of intellectual property, copyright, and Fair Use, and we need to make them the key points of our Library Research Lessons.
POSITIVE RESPONSIBILITY & SHORT LESSONS WITH SKILLS
I decided early on to approach these lessons with a positive responsibility focus, teaching students what TO DO rather than talking at them about what not to do. Thus, I chose the overriding concept of Academic Honesty on which to base my lessons. That decision has proven very successful with my middle school students—because I encourage them to be trustworthy, they rise to that expectation.
I’m a proponent of short, simple, relevant lessons that teach only what students need to perform the task at hand. Since we don’t expect a research assignment to be completed in a single day, Academic Honesty lessons can be spread out over the first few days of research to keep them very short and allow time for students to do their actual research. Each of my lessons follows a natural conceptual progression, from intellectual property, to copyright and Fair Use, then to public domain, and finally to plagiarism.
As teachers, we School Librarians know that students learn best when content and skills are taught in context. Each Academic Honesty lesson teaches a required documentation skill with its related concept and gives students time to apply them to a research activity. This is another smooth transition as students learn bibliographic citation, then in-document citation with notetaking, then citation of images and other non-text media.
A POSITIVE FOCUS ON INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
You may wonder why I begin with Intellectual Property and bibliographic citation of sources.
 Intellectual property is the overriding concept from which copyright, public domain, fair use, and plagiarism stem.
Intellectual property is the overriding concept from which copyright, public domain, fair use, and plagiarism stem.- Bibliographic citation needs to be the first thing students do with a source, because too often they forget to record the source and then can’t remember where they found information, either to return to it or to create their bibliography.
The positive focus is that giving someone credit for their intellectual property by citing them is the right thing to do. And I let students know that their products are their own intellectual property…and they certainly want credit for the work that they do!
COPYRIGHT & 3 METHODS OF NOTETAKING
The second Academic Honesty lesson transitions into the concept of Copyright & Fair Use, focusing on the legal rights conveyed to owners of intellectual property. During the lesson I use a 3-minute Common Sense Media video about Fair Use because I want students to understand why they can legally use other people’s copyrighted intellectual property for their school assignment. They need to understand this in order to know the difference between the 3 methods of note-taking from textual material: by quoting, by paraphrasing, and by summarizing.
I firmly believe if we take more time teaching and modeling note-taking with students, so they really learn and understand the 3 types, then we wouldn’t need to admonish them about plagiaristic writing. Quoting is usually well understood by older students, but I model an example to review it and explain how to include an in-line citation.
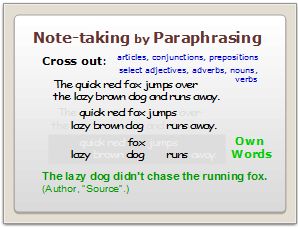 When I taught high school science, I was surprised how many students didn’t understand paraphrasing nor how to do it. Evidently this is a critical Information Literacy skill that we need to address earlier in their schooling as students begin gathering textual information. I spend time with students modeling how to paraphrase a short selection of text, and then helping them see that paraphrasing is still using someone else’s copyrighted intellectual property, so they need to cite the source in-line when they include the paraphrased material in their end product.
When I taught high school science, I was surprised how many students didn’t understand paraphrasing nor how to do it. Evidently this is a critical Information Literacy skill that we need to address earlier in their schooling as students begin gathering textual information. I spend time with students modeling how to paraphrase a short selection of text, and then helping them see that paraphrasing is still using someone else’s copyrighted intellectual property, so they need to cite the source in-line when they include the paraphrased material in their end product.
 Summarizing is often the lowest score on our State Reading Test, so after modeling an easy way to do it, a guided practice activity has students paraphrase and summarize excerpts from the Declaration of Independence and 3 famous Presidential speeches.
Summarizing is often the lowest score on our State Reading Test, so after modeling an easy way to do it, a guided practice activity has students paraphrase and summarize excerpts from the Declaration of Independence and 3 famous Presidential speeches.
Once students understand how note-taking relates to intellectual property and copyright, the third Academic Honesty lesson is about Public Domain & Creative Commons where the practice activity focuses on how to use images and other non-text media from these sources. I re-emphasize Academic Honesty and that they continue to use in-document and bibliographic citation for information or media that isn’t theirs—it’s still someone else’s original intellectual creation.
DON’T “DIS” HONESTY
Once students learn the “honest” practices, the last lesson, Academic Honesty and Plagiarism, explains that presenting someone else’s ideas, expressions, or creative work as your own is unethical. It’s an academically DIS-honest practice called plagiarism—and we all know it’s poor form to “dis” someone!
I find that discussing consequences of plagiarism is unproductive. Most students are eager to do what’s right, but a few would waste time on minutiae just to see what I’ll say. So when someone asks “What happens if I plagiarize?” I ask these questions back:
- Why do it wrong and then have to do it over?
- Why risk a teacher’s ill will and a bad grade when it’s so easy to do it right?
- Why not learn the right way now, when doing it wrong later on can endanger your entire future in college or a career?
I tell them, the only question I’ll answer is one about true learning, as in, “How do I properly express my knowledge?”
Lest you think my Academic Honesty unit sounds like a long drawn-out process, each lesson has fewer than a dozen slides as a brief beginning for the class period. Throughout the year I can use the short lessons to review pertinent concepts for a particular assignment. I’m not sure if my positive spin produces better student products, but I do know that students come away with a much more optimistic outlook about doing their research projects.
SOLVING THE PLAGIARISM PROBLEM
 My big concern about plagiarism is that we educators may be the problem. How can we discourage kids from plagiarizing when we offer them no opportunity for their own original expressions? When a teacher comes to us about resources for a student research project and we see that it’s low-level Bloom, just begging to be copied from an encyclopedia or a 3rd grader’s website, we, as the School Librarian, can diplomatically suggest ways to rework the topic so it requires more in-depth research, more higher-level thinking skills, and a genuine expression of a student’s own ideas and conclusions.
My big concern about plagiarism is that we educators may be the problem. How can we discourage kids from plagiarizing when we offer them no opportunity for their own original expressions? When a teacher comes to us about resources for a student research project and we see that it’s low-level Bloom, just begging to be copied from an encyclopedia or a 3rd grader’s website, we, as the School Librarian, can diplomatically suggest ways to rework the topic so it requires more in-depth research, more higher-level thinking skills, and a genuine expression of a student’s own ideas and conclusions.
Here’s an example. A 7th grade research project asks students to choose one Greek or Roman god or goddess, research their attributes from a couple books and websites, then create a written paper or a PowerPoint of the information. Ho Hum…I’m yawning and so will they.
My suggestion: compare a Greek/Roman god/goddess with a current popular star from TV/film/music/sports, explain the key attributes they share, and give an opinion on why these two were/are idolized. Every kid has a favorite star, someone they seek to emulate, and this assignment helps them examine the qualities they admire in this person and whether they really do want to be like them. They need to examine several Greek or Roman deities to decide who to compare, a more demanding analysis than the original assignment, and the compare/contrast with past and present can open their eyes to the human need to look outside ourselves for help in coping with life. Now how could anyone plagiarize that?
| You can find these Academic Honesty Lessons in my No Sweat Library store on Teachers Pay Teachers. |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |








