 To flourish in our modern global world, students need critical thinking skills, so educators are turning to inquiry based learning as the best approach. An Internet search explodes with models for teaching it.
To flourish in our modern global world, students need critical thinking skills, so educators are turning to inquiry based learning as the best approach. An Internet search explodes with models for teaching it.
What most teachers don’t realize is that their best resource already resides within their own building: the School Librarian.
School Librarians have been integrating curriculum content, critical thinking, and inquiry based learning for a long time, and this is exactly what educational researchers have recently discovered is needed.
ABOUT CRITICAL THINKING
The Foundation for Critical Thinking describes a critical thinker as one who:
- raises clear and precise questions
- gathers, assesses, and interprets relevant information
- derives well-reasoned conclusions, tested for relevance
- is open-minded, evaluating assumptions, implications, and consequences
- effectively communicates solutions to complex problems.
According to a recent article in The Hechinger Report, teaching critical thinking skills in isolation isn’t effective because students aren’t able to transfer skills between disciplines. Critical thinking is different within each discipline, so the skills needed for one subject area aren’t necessarily relevant to another subject area. Rather “the best approach is to explicitly teach very specific small skills of analysis for each subject.”
And this is where content knowledge becomes important. In order to compare and contrast, the brain has to hold ideas in working memory, which can easily be overloaded. The more familiar a student is with a particular topic, the easier it is for the student to hold those ideas in his working memory and really think. (Jill Barshay, 9/9/19)
ABOUT INQUIRY-BASED LEARNING
The crux of inquiry based learning is to pique a student’s curiosity and motivate the desire for answers—it is self-directed, not teacher-directed. The numerous models for inquiry based learning take students step-by-step through the process, but we can consolidate them all into 4 basic stages:
- Develop background knowledge & formulate focus questions
- Research to discover answers & build understanding
- Analyze & interpret information, then synthesize into a worthy action or product
- Impart results & reflect on the action/product and the process
By its very nature, inquiry demands that students apply critical thinking, or what educators often refer to as higher-order thinking, at every stage of the process. But, we cannot assume that our students have the necessary knowledge and skills to be successful at inquiry learning—it’s our responsibility to give them the guidance and time needed to learn.
Unfortunately, most teachers have no idea how to do this. Leslie Maniotes & Carol Kuhlthau summed this up in a Knowledge Quest article:
In typical schools of education teachers do not learn in their teacher education courses about the research process. …teachers are simply relying on their own experience in school to direct their approach to research. … Although teachers have good intentions, they don’t realize that their traditional research approach is actually not supporting student learning. (p9)
Maniotes & Kuhlthau point out that teachers are particularly ignorant about the difference between the exploration stage and the collection stage. During that exploration stage, students build the necessary background content knowledge so they can think critically throughout the rest of the process. When that stage is (too often) ignored, both the inquiry process and the resulting product suffer, and students are even less likely to learn, use, and transfer critical thinking skills.
THE GRAND INTEGRATOR: YOUR SCHOOL LIBRARIAN
The one person in the school who has all the necessary knowledge and training to guide students through inquiry learning is the School Librarian, who has examined multiple inquiry models as part of their graduate coursework. As Maniotes & Kuhlthau put it:
School librarians know the inquiry process like language arts teachers know the writing process and science teachers know the scientific method. (p11)
 This makes a School Librarian the perfect person to teach students an inquiry process for any subject area & product. A School Librarian excels at finding content—information and media—so can provide background knowledge that helps students through the crucial exploration stage. Plus, a School Librarian’s broad familiarity with everyone’s curriculum means s/he knows which critical thinking skills are relevant for each subject area.
This makes a School Librarian the perfect person to teach students an inquiry process for any subject area & product. A School Librarian excels at finding content—information and media—so can provide background knowledge that helps students through the crucial exploration stage. Plus, a School Librarian’s broad familiarity with everyone’s curriculum means s/he knows which critical thinking skills are relevant for each subject area.
School Librarians are authorities on critical thinking because the library’s Information Literacy curriculum is all about analyzing, evaluating, inferencing, synthesizing, and communicating complex information in multiple formats. Ann Grafstein of Hofstra University ties Info-Lit to critical thinking and to content knowledge:
Information literacy is a way of thinking about information in relation to the context in which it is sought, interpreted, and evaluated. …effective critical thinking crucially involves an awareness of the research conventions and practices of particular disciplines or communities and includes an understanding of the social, political, economic, and ideological context….
So, it is the School Librarian who can weave together relevant content, an inquiry process, and critical thinking skills to help students develop authentic, worthy products.
INFO-LIT = INQUIRY + CRITICAL THINKING + CONTENT
Through my years as a Middle School Librarian I use my Library Lesson Matrix to choose which strategies and skills are timely for each subject, at each grade level, across all grade levels, throughout the school year, in order to scaffold short Information Literacy lessons into any library visit.
My Library Lessons present inquiry strategies & skills in a way that students understand why, when, and how to use them. I believe students learn best with visual and aural “helpers”:
- I use infographics to illustrate strategies and processes.
- I use graphic organizers for conceptual knowledge because they help students develop the understanding for themselves.
- I use short videos (~3 minutes) to make explanations more engaging and understandable for students.
Here are some practices and resources that have been most successful with students, most appreciated by teachers, and have garnered positive feedback from my colleagues when teaching the 3 components of Information Literacy:
Research Process Models
 Planning and exploration must be the beginning of all effective inquiry-based learning. Simple brainstorming can be a quick & easy way to begin a project; however, implementing a model to guide students through the inquiry learning process assures a more successful outcome.
Planning and exploration must be the beginning of all effective inquiry-based learning. Simple brainstorming can be a quick & easy way to begin a project; however, implementing a model to guide students through the inquiry learning process assures a more successful outcome.
Popular models have from 5 to 20 different steps, so it’s important to choose one that is appropriate for the grade level, subject-area, and duration of the project.
To help School Librarians choose the appropriate design process for any inquiry assignment, download my comparative chart of 18 different research process models, available on my FREE Librarian Resources page.

A model created for my 6th graders is a simple way to “PACE” students through a project from planning to evaluation. Join my email group and you’ll gain access to my exclusive e-List Library where you can download my PACE PDF or editable DOCX graphic template and assessment rubric.
Search & Evaluation Skills
This Info-Lit component has 3 parts: source selection, search strategies, and resource evaluation. I like to use KWHL charts to guide students in the selection of materials suitable to their needs and abilities. I encourage them to use our library online subscription services for the most reliable information by showing this video:
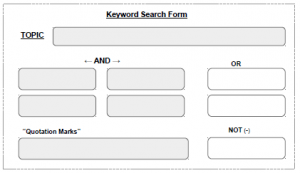 It’s crucial to allow students time to develop keywords so they receive useful results quickly. My successful keyword search form is available on my Free Librarian Resources page. For evaluation I use a simple ABC acronym. An earlier post explained why that’s all I use with my middle schoolers.
It’s crucial to allow students time to develop keywords so they receive useful results quickly. My successful keyword search form is available on my Free Librarian Resources page. For evaluation I use a simple ABC acronym. An earlier post explained why that’s all I use with my middle schoolers.
Academic Honesty
 It may surprise you that I don’t teach “plagiarism.” I’ve found it’s much more effective to give students the positive messages of Academic Honesty and teach them how to be legal & ethical, before getting to the cautions about plagiarizing. I begin each lesson with short relevant videos and then have hands-on activities, that introduce:
It may surprise you that I don’t teach “plagiarism.” I’ve found it’s much more effective to give students the positive messages of Academic Honesty and teach them how to be legal & ethical, before getting to the cautions about plagiarizing. I begin each lesson with short relevant videos and then have hands-on activities, that introduce:
- Intellectual Property and how to do bibliographic citation
- Copyright & Fair Use, along with proper note-taking and in-document citation
- Public Domain & Creative Commons, especially for images & media
| See my Intellectual Property, Copyright & Fair Use, and Public Domain & Creative Commons lessons in NoSweat Library, my TPT store. | ||
 |
 |
 |
RESOLVED…TEACHING CRITICAL THINKING & INQUIRY
Inquiry based learning and critical thinking should always begin with the School Librarian. Their raison d’être is helping students inquire and think critically to take in content knowledge and produce multimedia products that can change our lives.
Collaborative planning with teachers for inquiry based learning is essential, but it is hard to convince teachers to allow School Librarians more than a single day for these important Library Lessons. Those that do see their students produce better products more quickly, so they make the School Librarian part of their planning for the next such project. It’s even better when they tell others about how we contribute to their students’ research success!
Sources:
Barshay, Jill. “Scientific research on how to teach critical thinking contradicts education trends.” The Hechinger Report. Teachers College at Columbia University, September 9, 2019. https://hechingerreport.org/scientific-research-on-how-to-teach-critical-thinking-contradicts-education-trends/
Grafstein, Ann. “Chapter 1 – Information Literacy and Critical Thinking: Context and Practice: Abstract,” Pathways Into Information Literacy and Communities of Practice. Chandos Publishing, 2017. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780081006733000010
Maniotes, Leslie K.; Kuhlthau, Carol C. Making the Shift: From Traditional Research Assignments to Guiding Inquiry Learning. Knowledge Quest, v43 n2 p8-17 Nov-Dec 2014. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1045936.pdf
![]()







