 In our complex, information-rich, culturally diverse world, literacy is no longer just knowing how to read and write. Students need to understand and be proficient in Five Essential Literacies to be successful in our global society:
In our complex, information-rich, culturally diverse world, literacy is no longer just knowing how to read and write. Students need to understand and be proficient in Five Essential Literacies to be successful in our global society:
- Reading and Writing (the original literacy)
- Content/Disciplinary Literacy (content & thinking specific to a discipline)
- Information Literacy (the traditional library curriculum)
- Digital Literacy (how and when to use various technologies)
- Media Literacy (published works—encompasses all other literacies)
School Librarians can integrate at least one Library Literacy component into every class visit to the library, and I’m addressing each literacy in a separate blog post to offer examples and suggestions about how we might do that. Previous blog posts covered reading, content/disciplinary literacy, information literacy, and digital literacy, so this final post of the series looks at Media Literacy.
DEFINING MEDIA LITERACY
Media literacy during the last half of the 20th century focused primarily on print and television advertising, but in the 1990s the growth of computers and the Internet spurred the appearance of organizations such as the Center for Media Literacy, which promoted an expanded view of media literacy, incorporating digital citizenship.
With introduction of the iPhone (in 2007) and Android phones (in 2008), teens and children gained ready access to social media, so media literacy became a major issue for educators. Then the “fake news” epidemic thrust media literacy into the spotlight and elevated its status. Here are some recent definitions:
- Media literacy is the ability to identify different types of media and understand the messages they’re sending. Common Sense Media
- Media literacy encompasses the practices that allow the media consumer to access, critically evaluate, and create media to improve their communication effectiveness. Wikipedia
- Media Literacy is the ability to access, analyze, evaluate, communicate and create using all forms of communication. Natl. Assoc. for Media Literacy Education
Our National School Library Standards promote the Center for Media Literacy‘s definition:
- A framework to access, analyze, evaluate, create and participate with messages in a variety of forms—from print to video to the Internet. Media literacy builds an understanding of the role of media in society as well as essential skills of inquiry and self-expression necessary for citizens of a democracy.
Media is one of 5 specific literacies defined by our new National School Library Standards. Along with information literacy and digital literacy, the NSLS includes:
- Text literacy: ability to read, write, analyze, and evaluate textual works of literature and nonfiction as well as personal and professional documents. [related to reading literacy]
- Visual literacy: ability to understand and use images, including the ability to think, learn, and express oneself in terms of images. [related to content literacy, i.e. charts, graphs, maps, etc.]
Thus, we can build in students a broader understanding of Media Literacy by including civic responsibility and further, by embracing UNESCO’s 5 Laws of Literacy and its general definition of literacy: the ability to identify, understand, interpret, create, communicate, and compute, using materials associated with various contexts. (UNESCO 2006)
HOW TO INTEGRATE MEDIA LITERACY
School Librarians may wonder why the sudden pressure for media literacy, since our Info-Lit lessons on source evaluation presumably help students decipher ‘true’ from ‘not-true’ resources. Unfortunately, we rarely have an opportunity to deeply immerse students in skills like evaluation, plus, many students lack the command of subject matter that sifting for correct information requires. No form of website evaluation overrides a well-rounded knowledge of a topic or issue. A particularly interesting article explaining this is Yes, Digital Literacy. But Which One?
I believe media literacy encompasses all other literacies—either by type of material or skills needed:
- reading skills for printed media,
- content-area literacy to understand concepts and place them in context,
- information literacy for analyzing information, and
- digital literacy because so much media is now digitally presented.
Thus media literacy must be incorporated into all Library Lessons, because we always have students using or producing media products: print, audio, video, or graphic media presented through books, newspapers, magazines, social media, games, radio, television, videos or movies.
 Integrating media literacy can be a 5 minute “media moment” or an entire unit, depending on the purpose of the library visit. When creating these lessons, I focus on these 3 aspects of Media Literacy:
Integrating media literacy can be a 5 minute “media moment” or an entire unit, depending on the purpose of the library visit. When creating these lessons, I focus on these 3 aspects of Media Literacy:
- Media Messages – including celebrity endorsements and ads that persuade us to act or purchase
- Media Forms – the media products listed above, along with signs on businesses and billboards on the highway
- Media Footprint – personal communication & using social media
The breadth of media literacy makes it all the more important to integrate it with classroom content—with the standards and objectives the teacher is using for a unit—and to coordinate our Library Literacy Lessons with classroom activities. We need to not only teach students how to analyze media, but also how to effectively and ethically communicate their own narratives through various forms of media.
Media Literacy Through a Persuasive Book Talk
One simple way to integrate media literacy into a Library Lesson is through student-created booktalks. Whether written book reports, oral book summaries, podcast book reviews, or video booktrailers, these are all persuasive media forms.
 With 6th grade ELA students studying persuasion, I introduce 3 Key Questions about Media Messages:
With 6th grade ELA students studying persuasion, I introduce 3 Key Questions about Media Messages:
- Who created this message?
(Concept: All media messages are constructed.) - Why is this message being sent?
(Concept: Media messages are designed for influence or profit.) - How does this message attract my attention?
(Concept: Media messages use creative techniques to attract attention.)
Students begin to more deeply understand the 3 media questions and concepts as they create their own “media message”: a persuasive booktalk given as a graphic book preview poster, a graphic booktalk brochure, or a timed booktalk slideshow. I integrate the media literacy component with ELA concepts studied in the classroom: the tone & mood of their book will influence their choice of a persuasive appeal (logical, emotional, ethical) and guide their product choice.
RECOMMENDED ONLINE RESOURCES
I’m incorporating media literacy into more student lessons and to help me, I’m curating online resources. Here are a few that I recommend to help you construct your own Library Literacy Lessons.
Civic Online Reasoning or COR uses everyday digital content, the COR paper, and online assessments to engage learners in credibility decision-making around three COR Competencies: Who’s behind the information? What’s the evidence? What do other sources say? The free assessments include Google Docs assessments to copy and digital rubrics to download. These tasks are perfect for learning across the curriculum and especially for librarian-led learning.
 Common Sense Media‘s News & Media Literacy Curriculum Resources equip students with the core skills they need to think critically about today’s media. Classroom-tested lessons and teaching materials help students become smart, savvy media consumers and creators. Lesson plans on everything from fact-checking to clickbait headlines to fake news.
Common Sense Media‘s News & Media Literacy Curriculum Resources equip students with the core skills they need to think critically about today’s media. Classroom-tested lessons and teaching materials help students become smart, savvy media consumers and creators. Lesson plans on everything from fact-checking to clickbait headlines to fake news.
Project Look Sharp is a media literacy initiative of Ithaca College that develops and provides lesson plans, media materials, training, and support for the effective integration of media literacy with critical thinking into classroom curricula at all education levels, including integration with the new Common Core standards.
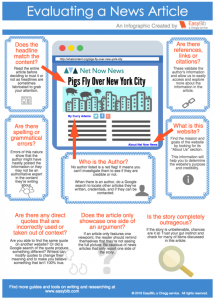
In an EasyBib blog post 10 Ways to Spot a Fake News Article, Michelle Kirschenbaum states, “You want to be informed, but a good deal of the information out there is incorrect or biased. Here are some things to keep an eye out for when reading a news article.” The infographic at right was created from the article.
The National Association for Media Literacy Education sponsors a yearly Media Literacy Week in the U.S. and Canada during the first full week of November. They have events and resources that can help introduce media literacy to your students early in the school year.
Feel free to suggest other resources I can add to this list!
This concludes my series of blog posts on the 5 Essential Literacies for Students. I invite readers to offer comments and suggestions about any or all of these literacies.







