We all give a School Library Orientation to our lowest-grade-level, new-to-the-school students so they can learn about their “new” school library, but how many of us have one for our returning students?
We all give a School Library Orientation to our lowest-grade-level, new-to-the-school students so they can learn about their “new” school library, but how many of us have one for our returning students?
A library orientation customized for each grade level is a powerful way to connect with students and teachers at the beginning of the school year. I discovered very quickly that the effort I expend on higher-grade-level orientations generates multiple benefits throughout the rest of the school year.
ADVANTAGES OF CUSTOMIZED ORIENTATIONS
- Rekindle interest in the library – The first library visit influences a student’s attitude toward subsequent visits during the remainder of the school year. Since so many schools now have a high level of student transience—mine is 34%—we also need to introduce the school library to a lot of brand new higher-grade-level students.
- Highlight new reading choices – New grade level = new subject content + increased maturity. Customized orientations can align with the new grade’s curricula and the changed interests of students, especially topics or formats they may not have noticed before.
- Establish silent sustained reading to the end of the period – The beginning of the school year is usually free of any benchmarks, testing, etc., so teachers are more willing to give us a whole class period for our orientation. In my case, ELA teachers want students to check out a fiction book, and because my library orientations focus on reading and narrative literature, students have time to become immersed in their book.
- Stimulate teachers to consider more library lessons – My ELA teachers appreciate that I structure my orientations to support their curriculum, so they allow me to give a Library Lesson at the start of each new unit of study. I also have unique orientations for Social Studies, for Science, for World Language, and for Art classes, which has encouraged those teachers to plan other Library Lessons throughout the school year.
- Use the same orientations every school year – With so many demands on a school librarian at the start of school, not having to create first-visit lessons is a time-saver and alleviates stress.
WHAT TO DO; WHAT TO AVOID
The key to a successful “returnee” orientation is to give students a stimulating, interactive, hands-on activity that is completely different from their previous grade‘s orientation. It should also revive prior knowledge and give a new perspective on the library and its resources.
 Don’t bore returning students with rules and procedures they already know. Summarize information on a Library Bookmark to be picked up at checkout. Give top grade level students a Library Brochure with resources for larger projects and planning their future. These two library info tools save time to allow for longer, more complex activities with higher-grade students, yet guarantee any new students learn our library expectations and can ask us specific questions later on for clarification.
Don’t bore returning students with rules and procedures they already know. Summarize information on a Library Bookmark to be picked up at checkout. Give top grade level students a Library Brochure with resources for larger projects and planning their future. These two library info tools save time to allow for longer, more complex activities with higher-grade students, yet guarantee any new students learn our library expectations and can ask us specific questions later on for clarification.
A new school year brings excitement but also apprehension. To relieve new-grade-level uncertainty, provide a familiar structure to returning student orientations. Of the four segments for my Library Lessons—direct instruction, modeling/guided practice, independent practice, and sharing/reflecting—I keep 3 of them the same as what students have already experienced:
- Direct instruction for returning student orientations is a review of safety procedures for fire drills and code Red—they’re too important to omit—and showing students the bookmark or brochure about library policies & expectations that they’ll receive at checkout.
a - Independent practice during any regular book checkout visit includes students browsing the shelves and choosing a fiction book they can enjoy reading. Since this is the reason the teacher brings them to the library for an orientation, I’m diligent to give students plenty of time to fulfill that purpose.
a - Sharing/reflecting for any regular book checkout visit is our standard checkout procedure where students read quietly while I invite each table to check out their selections. I encourage students to reflect on their book choice as they begin reading their new book so their book choices improve and their sustained reading time increases.
Such uniformity means I need only customize the modeling/guided practice segment of each grade’s orientation and allow returning students to fully engage in, and enjoy, their new group activity.
TRY DIFFERENT ACTIVITIES UNTIL SUCCESSFUL
We may need to try several orientation activities before discovering those that work best for each particular grade level of students:
- In-the-middle grades need reminders about what they learned the previous year, presented in a fun new way.
- Our highest grades need to see the library in a new way, a different perspective. They are the perfect “guinea pigs” to try out big changes in organization, materials, facility arrangement or technology.
Even after settling on the perfect lessons, be open to a new activity that might prove more engaging or relevant for a certain grade level. If you are a middle school librarian, the following ideas, which I’ve tried at various times, might work for you.
Seventh graders enjoy interactive game-like tasks that allow them to talk or move around. Library Bingo, Library Jeopardy, Scavenger Hunts, and Breakouts are all activities that refresh their library knowledge while constructively fulfilling their need for socializing. I do a Scavenger Hunt.
 My 7g Scavenger Hunt reviews various library locations, features new formats of reading materials students may have overlooked, and introduces books related to grade-specific subject content, like topical Dewey books for their first two Science units and the Special Collection of fiction & non-fiction books to support 7g Social Studies. It does get noisy, but students have a fun review, don’t get bored, and the Hunt sheet is handed in for their daily grade.
My 7g Scavenger Hunt reviews various library locations, features new formats of reading materials students may have overlooked, and introduces books related to grade-specific subject content, like topical Dewey books for their first two Science units and the Special Collection of fiction & non-fiction books to support 7g Social Studies. It does get noisy, but students have a fun review, don’t get bored, and the Hunt sheet is handed in for their daily grade.
(Clipboards for students to write on are invaluable for this activity.)
The key to a successful scavenger hunt is to have the same number tasks as library tables. Each group begins with the same numbered task as their table number, which takes students to different library locations and avoids jostling and overcrowding.
Eighth graders prefer sophisticated tasks that entail analysis and application, and provides guidance but not overt supervision. Speed Dating Fiction, Progressive Dinner of Tasty Reads, Breakouts, Playlists/HyperDocs, and Viewing Book Trailers with QR codes are all popular with this age. Using QR codes to view Book Trailers finally captured my 8th graders attention; I give details about it in an earlier post.
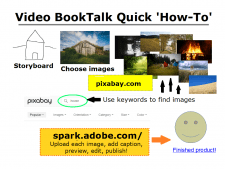 I briefly show students how easy it is to make a video book-talk using copyright-free pictures and an online video creation tool, then play my 40-second sample. Since the first ELA project is a video book-talk, teachers appreciate my “sneak peak” to get students excited to do their own. Then they use QR codes to watch book trailers which provide an introduction to new reading choices appropriate to 8g maturity and curricula, like our selection of high school State Reading List books and the Special Collections of fiction and non-fiction books that support 8g Social Studies.
I briefly show students how easy it is to make a video book-talk using copyright-free pictures and an online video creation tool, then play my 40-second sample. Since the first ELA project is a video book-talk, teachers appreciate my “sneak peak” to get students excited to do their own. Then they use QR codes to watch book trailers which provide an introduction to new reading choices appropriate to 8g maturity and curricula, like our selection of high school State Reading List books and the Special Collections of fiction and non-fiction books that support 8g Social Studies.
PROGRESSIVELY BUILD YOUR ORIENTATION REPERTOIRE
I know you, too, can reap the benefits of customized library orientations. If you are a new librarian or starting at a new school, you can begin as I did: I created an orientation for our lowest-grade-level students—6th graders—but presented it to all the grades. The next year’s incoming 6g got that same orientation, but I created a new orientation for the next higher grade level and presented it to both 7th & 8th graders. Then the third year, the incoming 6g got the original orientation, new 7g students got the second orientation, and I created another new orientation just for our highest grade level 8g students. Other than a couple adjustments for 8g, I give the same 3 orientations every year and it’s always a new experience for each grade level of students. If you have more than three grade levels, just keep going until you have a unique orientation for all the grade levels in your building!
My success with Customized Library Orientations means I never have to convince the English Language Arts teachers to bring their classes to the library at the start of school. In fact, they seek me out to schedule their visits the week before school begins!
| Get my 7g Library Orientation or 8g Library Orientation through my NoSweat TPT store, or save with the 678 Orientation bundle. | ||
 |
 |
 |