 Fixed vs. Flexible Scheduling for school libraries has long been controversial, and AASL now recommends we implement “Responsive scheduling”. The purpose for library scheduling is often misunderstood by school administrators, by teachers, and even by School Librarians, so it’s time to take a fresh look.
Fixed vs. Flexible Scheduling for school libraries has long been controversial, and AASL now recommends we implement “Responsive scheduling”. The purpose for library scheduling is often misunderstood by school administrators, by teachers, and even by School Librarians, so it’s time to take a fresh look.
To better understand the issue of fixed or flex or responsive scheduling, it may help to see how far we’ve come, and where we are now, so that we can effectively work toward where we need to be.
A SHORT HISTORY OF LIBRARY SCHEDULING
Fixed scheduling was originally a non-negotiable schedule of library visits set by school administration. Lessons came from a specific, fixed, scope-and-sequenced Library curriculum of what students needed to know about the library, just as English, Math, Social Studies, and Science were separate curricula. There was no coordination of Library skills with what was happening in classrooms, but that seemed OK, since none of the subject areas were coordinated either.
For the next 30 years we tried to coordinate and integrate curriculum to improve student learning, like adding literature, art, and music to Social Studies. Along the way we increased the use of technology and added authentic project-oriented assessment.
 Educational advancements increased use of the school library, highlighting inadequacies in student information literacy skills and the need for an improved library program to address these skills at point of need. AASL’s Information Power (published in 1988 and republished in 1998) promoted the integration of library skills into the curriculum and a flexible approach to library use for the teaching of these skills. To make that happen, librarians and teachers would collaborate on how and when to teach what.
Educational advancements increased use of the school library, highlighting inadequacies in student information literacy skills and the need for an improved library program to address these skills at point of need. AASL’s Information Power (published in 1988 and republished in 1998) promoted the integration of library skills into the curriculum and a flexible approach to library use for the teaching of these skills. To make that happen, librarians and teachers would collaborate on how and when to teach what.
THE FLEX APPROACH: THE PROS & CONS
No more stand alone library lessons taught in isolation from other subjects. No more classes dropped off by teachers at prescribed times each day of each week. School Librarians would now flexibly schedule classes into the library when they needed to be there, for a few days in a row if necessary, and take time to plan with teachers to create lessons that integrate library skills into classroom activities.
Here’s where some misunderstanding arose. If fixed scheduling denied us power over our schedule, flex scheduling can also take away our decision-making power. If we’re told we can’t have any schedule at all, that we need to provide unlimited access, to anyone, anytime, to do anything, well, that isn’t what flex schedule means.
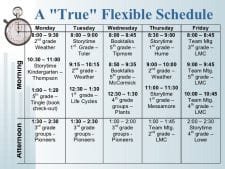 The key word is flexible. It means that, rather than being forced to accept specific classes on a regular schedule, WE determine who uses the library and when. It means we decide when a class needs to be in the library, and it means we can even have a fixed schedule for certain classes, because we have decided that is what students need.
The key word is flexible. It means that, rather than being forced to accept specific classes on a regular schedule, WE determine who uses the library and when. It means we decide when a class needs to be in the library, and it means we can even have a fixed schedule for certain classes, because we have decided that is what students need.
True flex scheduling means we can say yes or no to casual drop-ins or last-minute requests, because we have a class scheduled to visit which requires our full attention, especially when we don’t have an aide to assist with book checkout. It also means that students working on projects we’ve had a part in teaching can come to the library at any time even if the class isn’t scheduled.
BENEFITS OF A COMBINATION FIXED/FLEX
A fixed schedule provides more opportunities for teaching and reinforcing library skills, so we must know our school’s curricula very well and develop a wide repertoire of activities to keep students engaged. Fixed schedules demand that we become as flexible as possible to plan with teachers and integrate curriculum into our library lessons.
Flex scheduling promotes integration of library skills into classroom activities; however, flexible schedules demand that we regularly plan with teachers and schedule classes for library and research skills. Either way, we must push ourselves to become a better professional. As fixed scheduled teachers work with us, they begin to see the benefits of having a flexible library schedule, so they can become our best allies when we ask administration to move toward flex scheduling.
I began my school library career with completely flexible scheduling, but after a couple years it became problematic. Once I understood what true flex scheduling meant, I created a combination fix/flex schedule that works for our school:
- ELA classes come to the library on a set day every other week for book checkout and DEAR time (silent reading). We collaborate on a schedule so one week 7g & 8g classes visit on Tuesday & Wednesday, then the following week SpEd/ELL and 6g visit on Thursday and Friday. I can adjust ELA visit day if the library is otherwise needed: we switch to another open day that week, or they get books & return to the classroom for DEAR time, or the teacher sends a few students at a time for a new book.
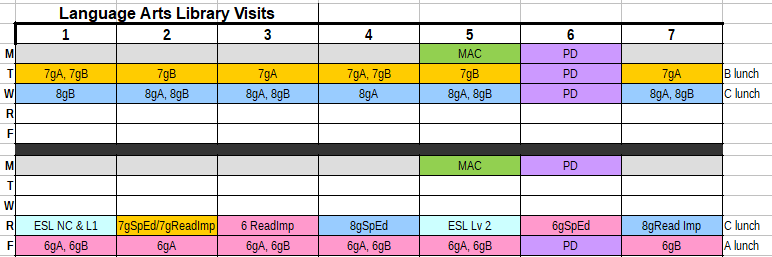 linebreak
linebreak - With 5 contiguous open days—Thursday through Wednesday, every other week, I can schedule other subject classes into the library for lessons and research assignments.
- I can reserve Monday for library administrative work, for planning, and for collaboration with teachers, unless it’s essential for a teacher to bring students in that day.
- Recurring yearly lessons, such as my Dewey Decimals Lesson with 6g and 7g Math classes, my Online Subscription WebQuests with 6g and 7g Social Studies, my Cloud Computing Lesson with Spanish & Art classes, and my Digital Citizenship Lessons, are all scheduled with teachers at the start of each grading period to be sure there are no conflicts with newly planned projects that may need to use the library and its resources.
This combination (or semi-fixed/flex) scheduling worked well in my School Library for over a decade from the early 2000s.
“RESPONSIVE” SCHEDULING FOR THE 2020s
AASL Standards for the 21st Century Learner in Action (2009) offered little about scheduling other than consistent use of the term equitable access. However, AASL issued a Position Statement on Library Scheduling in 2011, revised in 2014, which was printed in the new National School Library Standards (2018, p216), about “flexible scheduling”:
Classes must be flexibly scheduled to visit the school library on an as-needed basis to facilitate just-in-time research, training, and use of technology with the guidance of the teacher, who is the subject specialist, and the librarian, who is the information-search process specialist. … Regularly scheduling classes in the school library to provide teacher release time or preparation time prohibits this best practice.
 Then in 2018, “flexible scheduling” was revisited to better align with the new Standards. The new AASL Position Statement on Library Scheduling was submitted to the board and approved in June, 2019. Their new recommendation is for “responsive scheduling”:
Then in 2018, “flexible scheduling” was revisited to better align with the new Standards. The new AASL Position Statement on Library Scheduling was submitted to the board and approved in June, 2019. Their new recommendation is for “responsive scheduling”:
Scheduling of classes should allow flexible, open, unrestricted, and equitable access on an as-needed basis to facilitate just-in-time research, training, and utilization of technology with instruction from the school librarian and the content-area educator. The practice of scheduling classes in the school library on a set schedule to provide educator release or preparation time inhibits best practice by limiting collaboration and co-teaching opportunities between the school librarian and classroom educator.
Responsibility for responsive scheduling is to be “shared by the entire school community: the local educational agency, district administration, principal, school librarian, educators, the school library support staff, parents, and learners.” We School Librarians can use this section when we approach our principals for a more flexible schedule, and give them something to take higher up.
This new Position Statement on School Library Scheduling is a critical document for School Librarians “desiring to fully achieve a collaborative and integrated school library philosophy.” It emphasizes the importance of collaborative planning and helps us promote our Library Lessons as “an essential and integral part of all classroom curriculum.” I encourage all of us to print out this 3-page PDF document to show to our principals and our teachers and to develop a new “elevator pitch.”
With this new Position Statement we may need to make changes in our policies & procedures. I’d love to have an aide to help with book checkout and incidental student interaction while I’m teaching classes, but know that’s not fiscally likely. So, I set up a self-checkout station and teach students how to use it, having eliminated overdue fines and increased book limits to remove barriers for making this work.
I use the Open Dyslexic font for print and digital documents to make it easier for all students to read materials. I create videos answering some common questions students ask about the library and its resources, putting them on the School Library Website, so students can find answers when I’m unavailable.
I have computer administrators set the student browser homepage to the School or District Library Website so our virtual library is the first resource students see. This will ease student access to searching for books, using research databases, and locating Resource Lists, library guides, and other assignment helpers.
I’m sure there are other considerations I’ve not even thought about. If you have suggestions, please add them to the comments!
References:
AASL Board of Directors Meeting, ALA 2019 Annual Conference, Washington, DC June 20 – 25, p46-50
AASL Position Statement on School Library Scheduling




